This work involves laser welding austenitic and duplex stainless steel to zinc coated mild steel more specifically 1 2mm v1437 which is a volvo truck coiporation rephosphorised mild steel.
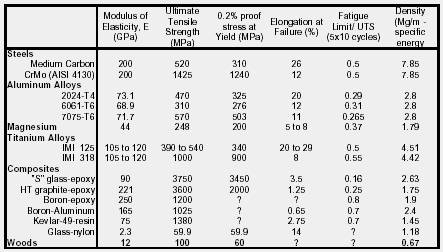
References material properties sheet metal fatigue.
This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
One of the intriguing factors about fatigue development is that fatigue cracks can be initiated and propagated at stresses well.
By this we can be able to take necessary corrective action in design maintenance and operation to avoid another failure.
The work investigates both tensile and lap shear properties of similar and dissimilar metal laser welded butt and lap joints with the majority of the investigation concentrating on the fatigue properties.
Certain materials have a fatigue limit or endurance limit which represents a stress level below which the material does not fail and can be cycled infinitely.
Typical s n curves endurance limit.
The red points in the chart represent the cyclic stress for each test and the number of cycles at which the specimen broke.
Fatigue is a failure mechanism that involves the cracking of materials and structural components due to cyclic or fluctuating stress.
Metal failure is a common phenomenon when a metal component is subjected to cyclic stresses or overloading.
Mridha in reference module in materials science and materials engineering 2016.
Metallic materials include elemental metal and compound or alloy.
In materials science fatigue is the weakening of a material caused by cyclic loading that results in progressive and localized structural damage and the growth of cracks.
In this article we discuss how to perform a metal fatigue failure analysis to determine the reason for the failure.
With the aid of a diagram explain the micro structure of.
If the applied stress level is below the endurance limit of the material the structure is said to have an infinite life this is characteristic of steel and titanium in benign environmental.
Discuss the differences between pearlite bainite and martensite in carbon steels.
Metal fatigue analysis handbook 2012.
Fatigue is defined as a process of progressive localized plastic deformation occurring in a material subjected to cyclic stresses and strains at high stress concentration locations that may culminate in cracks or complete fracture after a sufficient number of fluctuations.
The curve which is fitted through these clusters known as an s n diagram stress vs.
Number represents the statistical behavior of the fatigue properties of that specific material at that specific strength level.
While applied stresses may be tensile compressive or torsional crack initiation and propagation are due to the tensile component.
Sketch the microstructures and discuss the properties of each phase e g.
There are 86 metals with distinct characteristic properties and a limited number of these metals have engineering importance.
Once a fatigue crack has initiated it will grow a small amount with each loading cycle typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface.